
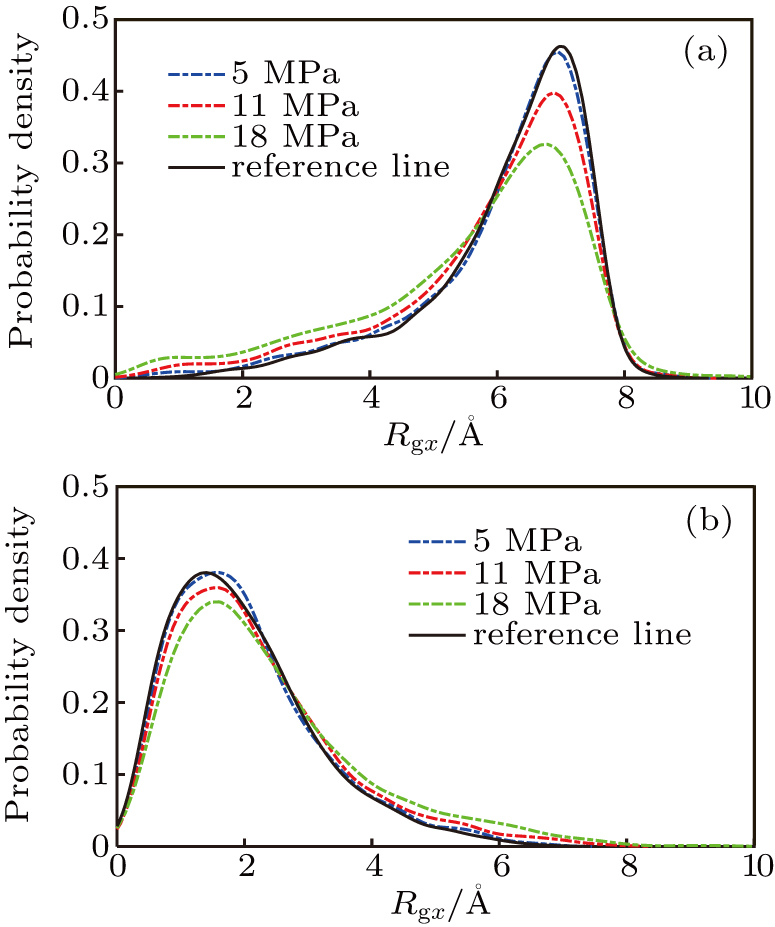
In terms of decreasing friction and adhesion, surface-coating technologies like self-assembled monolayer (SAM) coating, diamond-like carbon (DLC) coating and ceramic coating have been proven to be effective methods to improve the surface properties of metal mold insert and reduce interfacial interactions. The friction and adhesion at the interface between the polymer and mold insert are the fundamental limiting factors for the high-quality replication of products. Studies have shown that most of the deformations are mainly caused by friction, adhesion and the thermal contraction force. The demolding process plays an important role in the high-quality replication of the microchannels.ĭuring the demolding process, the main deformations of the channels are warping, stretching, and surface burr. Its process mainly includes four stages as the filling, the packing, the cooling and the demolding. Injection molding technology is one of the main methods for microfluidic chip manufacturing, which has the advantages of high precision, low cost, high efficiency, and short cycle. The performance of the microfluidic chip thus largely depends on the replication quality of these channels. The main functional structure of the microfluidic chip is the microchannel, as to complete fluid filling, sample separation and detection. Microfluidic chips have been widely used in life science, chemical analysis, medical detection and other fields. In a word, DLC-coating treatment on the mold insert has great application potential for improving the demolding quality of injection-molded microfluidic chips. However, the change in the elastic recovery of the polymer channel was increased, and the opening width became larger. The treatment of DLC coating could also significantly reduce the change in the gyration radius of polymer molecular chains, so the morphology of the polymer channel could be maintained well. Moreover, common channel defects such as molecular chain separation, surface burrs and necking did not occur. The results showed that the non-bonded interfacial interaction energies could be significantly reduced by DLC-coating treatment on the mold insert. In particular, the non-bonded interfacial interaction energy, elastic recovery and gyration radius of polymer molecular chains were further studied. The channel qualities of polystyrene (PS), polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA), cyclic olefin copolymer (COC) and polycarbonate (PC) were analyzed after demolding with nickel (Ni) and DLC-coated mold inserts, respectively.

In this study, molecular dynamics (MD) simulations on the demolding process were carried out to investigate the influence of diamond-like carbon (DLC) coating on the channel deformation. As an important stage, the demolding process in injection molding will directly affect the quality of the functional unit of microfluidic chips (polymer microchannels), thus limiting the realization of its functions. Injection molding is one of the main techniques for manufacturing microfluidic chips.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
